In this post I try to cover the Item Reordering Policies in Business Central System. Keeping the right stock in your warehouse is always a challenge. Too much stock means money is stuck on shelves. Too little stock means unhappy customers.
That is where Reordering Policies in Business Central help. They are rules that tell the system when and how much to order.
In Business Central, the most common 3 policies are as follows:
- Fixed Reorder Quantity
- Lot-for-Lot
- Maximum Quantity
Other than this “Order” policy is there.

Now let us see each one step by step in detail.
Table of Contents
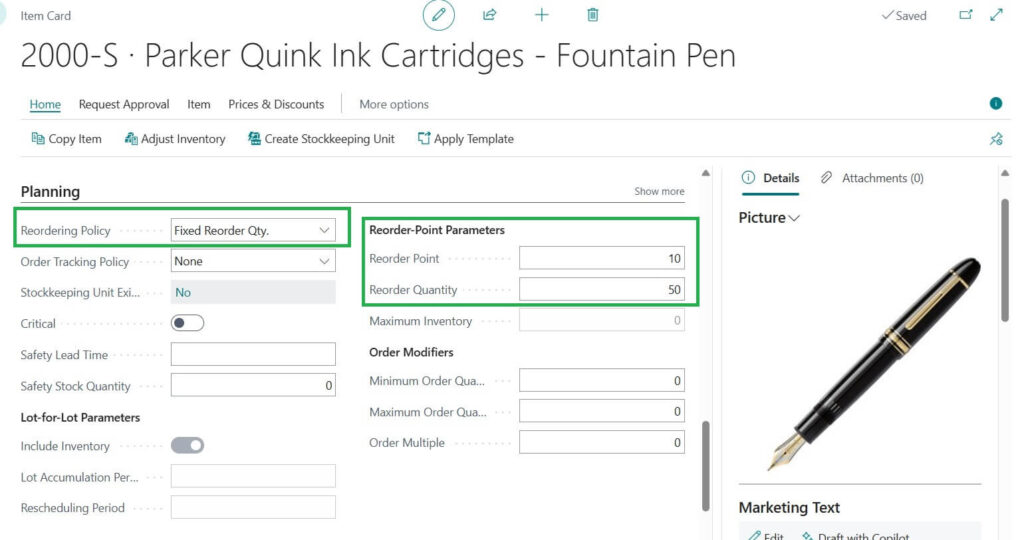
1. Fixed Reorder Quantity
With Fixed Reorder Quantity method, you always order the same fixed number of items when your stock goes below a set level.
What it means:
You decide a fixed number of units to order whenever your stock drops below a certain level.
Example:
If you set the reorder quantity to 50 and your stock falls below 10, Business Central suggests ordering 50 every time.
Best for:
Items with steady demand (like office supplies, water bottles, or packaging boxes).
Products you prefer to buy in bulk because it’s cheaper or easier.
Note: If demand suddenly drops, you might end up with too much stock.
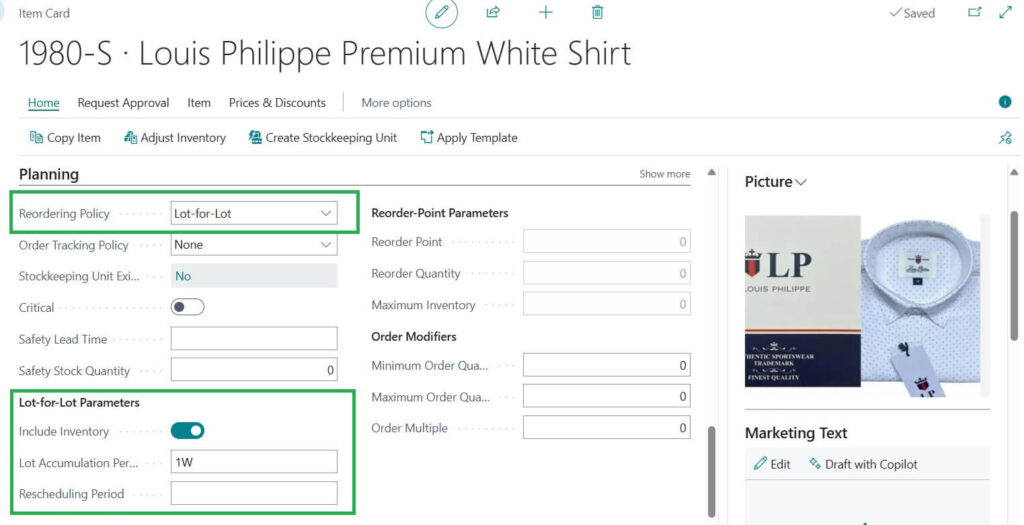
2. Lot for Lot
In the case of Lot for Lot reordering policy , the system orders exactly what is needed to cover demand. Nothing more, nothing less.
What it means:
The system orders exactly what you need based on current demand.
Example:
Simple scenario used as follows
Customer order = 120 T-shirts -> System suggests = 120.
Next week, order = 80 T-shirts -> System suggests = 80.
Best for:
Items where demand changes often, and you do not want extra stock lying around.
High value items where you do not want to hold too much stock.
Note: It can create lots of small purchase or production orders if demand is very frequent.
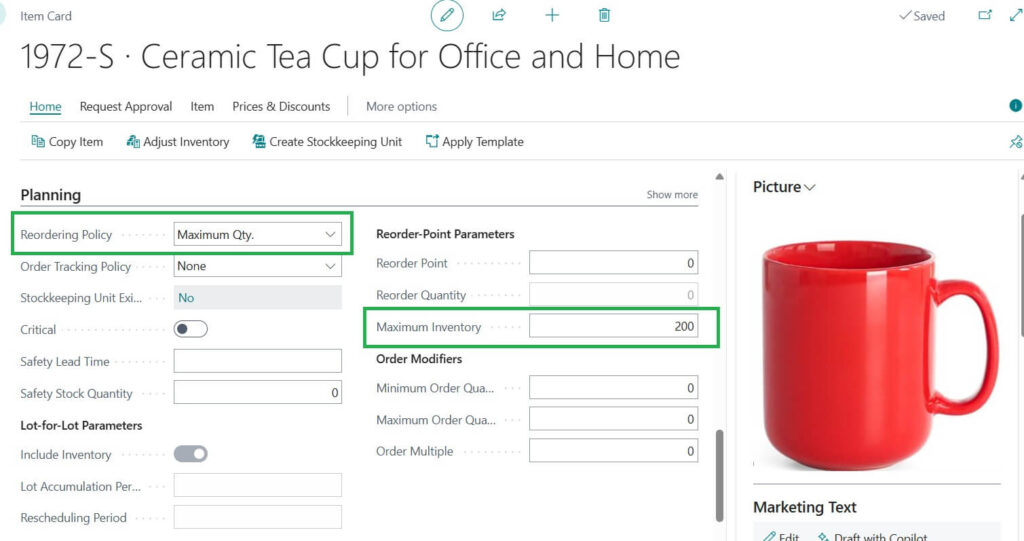
3. Maximum Quantity
Maximum Quantity policy, you set a maximum stock level. Whenever stock falls, Business Central suggests ordering enough to bring it back up to that max.
What it means:
You decide a maximum stock level, and whenever stock drops, the system suggests refilling up to that level.
Example:
Simple scenario used as follows
If your maximum stock is 200 mugs and you currently have 75, Business Central suggests ordering 125 to bring it back up to 200.
Best for:
Fast moving items where you always want a buffer (like groceries, beverages, or daily use products).
Situations where you have limited storage space and need to cap inventory.
Note: If demand is unpredictable, you might end up placing frequent orders.
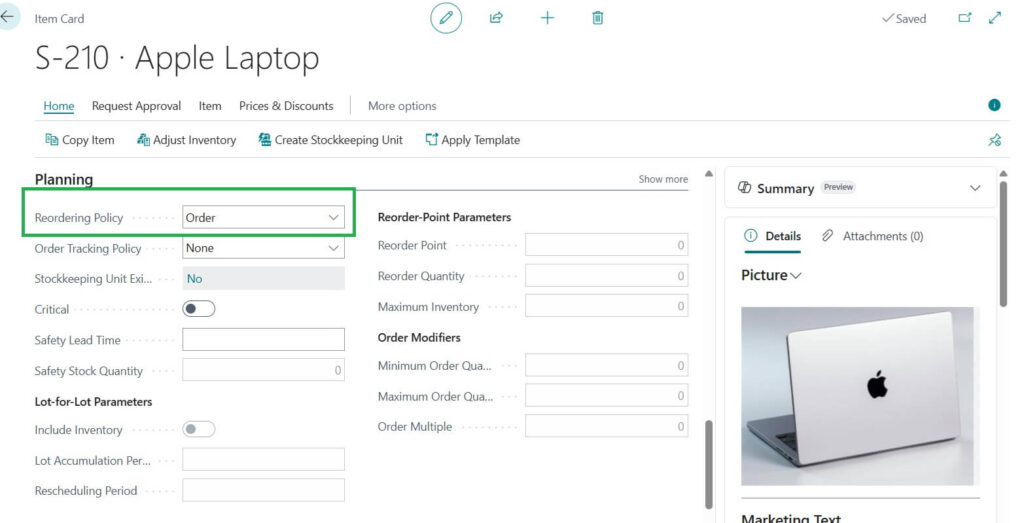
4. Order
Order reordering policy is the system suggests one order for every demand.
What it means:
if a sales order, production order, or service order needs items, Business Central will recommend creating a matching supply order for exactly that demand.
Example:
Simple scenario used as follows
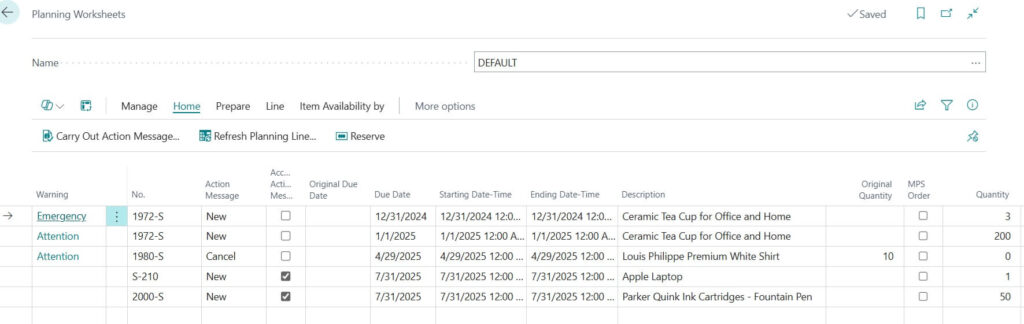
If a customer orders 25 laptops -> BC suggests an order for 25 laptops.
If another customer orders 10 laptops -> BC suggests another separate order for 10 laptops.
So, each demand gets its own supply order.
Best for:
The Order policy is best suited for:
Make to Order businesses : when you only buy or produce after a customer places an order.
Expensive or customized items : where holding stock is risky or costly.
Low volume, high value products : like machinery, special parts, or tailored goods.
Note:
- May lead to many small orders.
- Not efficient for items with frequent, small demands.
- Can increase purchasing or production costs due to multiple transactions.
Quick Comparison : Reordering Policies
Following table shows the quick comparison between each reordering policies
| Reordering Policy | How it works | Example | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Reorder Quantity | Orders the same fixed amount | Always order 50 pens | Steady demand |
| Lot for Lot | Orders exactly what is needed | Order 120 shirts for an order | Changing demand |
| Maximum Quantity | Refills stock to max | Keep mugs at 200 | Fast moving items |
Choose Order Policy when stock holding is not practical, and you only want to act when there is real demand.
FAQ : Frequently Asked Questions for Item Reordering Policies in Business Central
Following are some of the FAQs here for your reference
Item reordering policies are rules that help Business Central suggest how much stock to order and when. They prevent overstocking or running out of items.
This policy always orders a fixed number of items whenever stock drops below a set level. Best for steady demand products.
Lot-for-Lot orders exactly what is needed based on current demand, making it flexible for changing customer needs.
Use Fixed Reorder Quantity for steady demand.
Use Lot-for-Lot for unpredictable or seasonal demand.
Use Maximum Quantity for fast-moving or daily use items.
This policy refills stock up to a set maximum whenever levels go down, keeping a buffer for fast-moving goods.